Choosing the right Gaas Focus Lens is a critical step in optimizing optical systems for various applications. With so many options available on the market today, it can be overwhelming to determine which lens will best meet your specific requirements. Whether you are working in the fields of telecommunications, medical imaging, or laser applications, the performance of your optical system hinges significantly on the characteristics of the Gaas Focus Lens you select.
Understanding the key factors that influence the selection process is essential for achieving the desired outcomes in your projects. Parameters such as wavelength range, numerical aperture, and lens geometry play crucial roles in defining the lens's functionality and performance. By carefully considering these aspects, you can ensure that your chosen Gaas Focus Lens aligns perfectly with your optical needs, thereby enhancing the efficiency and effectiveness of your systems.
This guide aims to provide insights into the essential criteria for selecting the appropriate Gaas Focus Lens, empowering you to make informed decisions that will enhance your optical endeavors. With a focus on performance and compatibility, we will explore the critical elements that will help streamline your selection process and ultimately lead to more successful outcomes.

Gallium arsenide (GaAs) focus lenses have become increasingly significant in various optical applications, particularly in high-performance environments such as telecommunication systems, laser optics, and photonic devices. These lenses are prized for their superior material properties, which include higher electron mobility and a direct bandgap, making them ideal for devices that require efficient light absorption and emission. According to a report from the Optical Society of America, the demand for GaAs components in optical applications is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 8% through 2025, emphasizing the lens's importance in advanced technology.
When considering GaAs focus lenses, understanding the refractive index and transmission characteristics is crucial. The refractive index of GaAs typically ranges between 3.3 to 3.5 at room temperature, which significantly affects the focal length and overall efficiency of the lenses. In addition, GaAs lenses exhibit excellent transmission in the infrared spectrum, with transmission rates exceeding 90% at certain wavelengths. This property is essential for applications in infrared imaging and high-power laser systems, as detailed in the latest photonics industry report by Research and Markets, which highlights that the growth in infrared technologies will further elevate the need for specialized optical components.
Furthermore, the selection of the right lens must consider specific application requirements, such as wavelength range, power handling capacity, and mechanical durability. As the industry moves towards miniaturization and increased demand for efficient optical systems, the role of GaAs focus lenses will become even more pivotal. Industry forecasts suggest that by 2027, the optical components market, including GaAs lenses, will reach a valuation exceeding $50 billion, reflecting the ongoing advancements and growing reliance on state-of-the-art optical technologies.
When selecting a GaAs focus lens for optical applications, understanding key technical specifications is crucial. One of the primary considerations is the lens's focal length, which significantly influences the system's resolution and depth of field. According to a report published by the Optical Society, a focal length range of 8 mm to 30 mm is optimal for many laser applications, allowing fine-tuning for precision focusing. Moreover, as the focal length increases, the system's magnification varies, directly impacting the quality of the image produced.
Another vital specification is the numerical aperture (NA) of the lens, which determines the light-gathering ability and the resolving power. A higher NA, typically greater than 0.5, is generally preferred for applications requiring high-resolution images. Data from the International Society for Optical Engineering indicates that lenses with higher NA values can capture more light and provide better performance in low-light conditions.
Furthermore, lens material and coating play significant roles in transmission efficiency. GaAs lenses often exhibit high transmittance in the mid-infrared wavelength ranges, typically around 1.5 to 20 microns, making them suitable for a variety of scientific and industrial applications. Comprehensive understanding of these specifications ensures that users can effectively match their optical needs with the appropriate GaAs focus lens.
The choice of a GaAs focus lens
over traditional lens types can significantly affect optical performance, particularly in applications requiring
high precision. Gallium arsenide (GaAs) lenses are known for their superior performance in infrared applications,
offering better transmittance and focus stability compared to conventional materials like glass or plastic.
According to a report by the Optical Society, GaAs lenses can deliver up to 80% transmission efficiency
in the 900 to 1800 nm wavelength range, making them ideal for laser systems and telecommunications.
This is particularly important in industries where precision is critical, such as medical devices and communication technologies.
When comparing GaAs focus lenses to other lens materials, it is essential to consider factors such as
thermal stability and wavelength response.
GaAs has proven to possess excellent thermal conductivity, minimizing aberrations that are influenced by
temperature fluctuations. Furthermore, unlike typical glass lenses, GaAs lenses maintain consistent
performance across a greater range of temperatures, a crucial aspect for applications in harsh
environments. A study published in the Journal of Applied Physics highlights that GaAs can withstand
temperature variations of up to 200°C better than
conventional lens materials.
Tips: When selecting
a GaAs focus lens, consider the specific wavelength range and application requirements to ensure optimal
performance. Additionally, consult with optical experts to understand how the lens material will interact
with your entire optical system to achieve the best results. Always assess the environmental conditions
where the lens will be used, as this can significantly impact longevity and effectiveness.
When selecting GaAs focus lenses for specific optical tasks, several factors come into play. The wavelength of the light being used is crucial; GaAs lenses perform optimally at certain wavelengths, which should align with your project's requirements. Additionally, the application environment, whether it be high or low temperature or exposure to aggressive chemicals, can influence the choice of material and lens design. Understanding the optical properties and thermal characteristics of GaAs is essential for ensuring compatibility with your system.
Tips: Consider conducting a thorough analysis of your optical system before making a selection. This includes measuring light intensity, understanding your imaging requirements, and evaluating the size and shape of the area to be focused.
Another important factor is the lens shape and design, which can affect focusing capabilities and image quality. For instance, aspheric lenses can minimize spherical aberrations and improve performance in high precision applications. Assessing the specific optical tasks, such as beam shaping or collimation needed for your project, will guide you in selecting the most suitable lens configuration.
Tips: Engage with simulation tools to model the lens performance in your application. Such tools can provide insights into the focal depth and aberration levels, allowing for a more informed decision when choosing the right lens for your needs.
| Lens Type | Focal Length (mm) | Diameter (mm) | Wavelength Range (μm) | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Convex Lens | 10 | 25 | 1.0 - 1.5 | Laser Focusing |
| Concave Lens | 20 | 30 | 1.5 - 2.5 | Beam Divergence |
| Aspheric Lens | 15 | 20 | 0.8 - 1.2 | High-Precision Imaging |
| Cylindrical Lens | 50 | 40 | 1.2 - 1.8 | Line Generation |
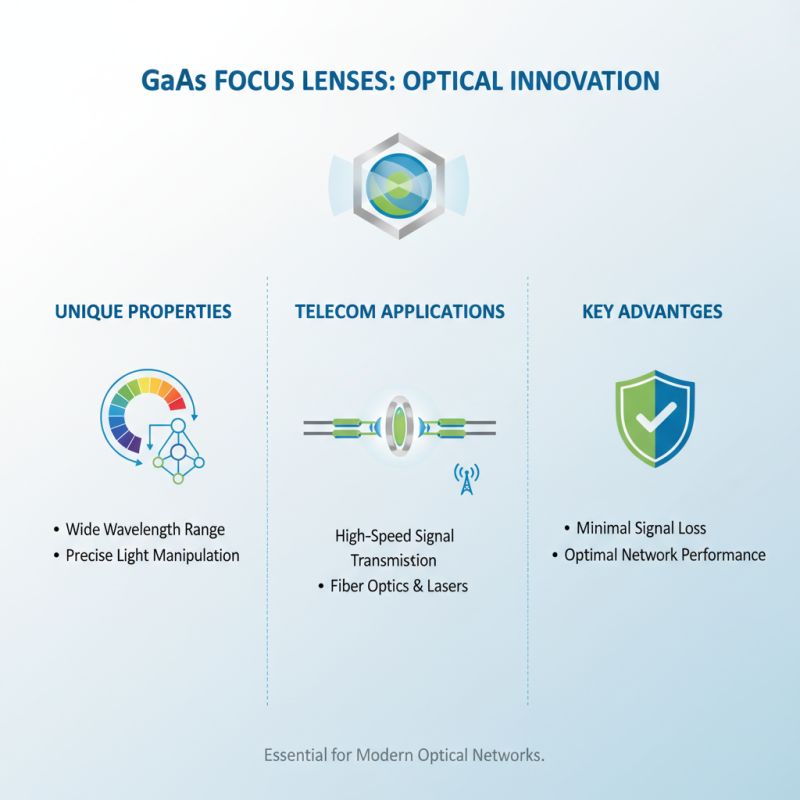
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) focus lenses are increasingly popular in various industry applications due to their unique optical properties. One significant use case is in telecommunications, where these lenses facilitate high-speed signal transmission through fiber optics. Their ability to handle a wide range of wavelengths makes GaAs lenses ideal for devices that require precise light manipulation, such as lasers used in communication systems. This precision ensures minimal signal loss and optimal performance, making GaAs lenses an essential component in modern optical networks.
Another prominent application of GaAs focus lenses is in the field of imaging and sensing technologies. These lenses are utilized in infrared cameras and sensor systems, where they enhance image resolution and sensitivity. The infrared capabilities of GaAs lenses enable accurate temperature measurement and detection of thermal signatures in various environments, from industrial monitoring to medical diagnostics. The versatility of GaAs lenses in these applications highlights their crucial role in advancing optical technologies across multiple sectors, providing enhanced functionality and efficiency.