When selecting the optimal Gaas Focus Lens for your optical applications, understanding the intricacies of lens performance and material properties is crucial. Dr. Emily Carter, a noted expert in optical engineering, emphasizes, "The choice of a Gaas Focus Lens can significantly impact the efficiency and precision of your optical system." With the unique advantages of Gallium Arsenide, such as a higher refractive index and excellent thermal stability, selecting the right lens becomes an essential step in enhancing optical performance.
In the ever-evolving landscape of optical technologies, the Gaas Focus Lens stands out due to its specialized capabilities tailored for a variety of applications, including telecommunications and laser systems. This lens type is revered for its ability to focus light with exceptional accuracy while minimizing distortion, making it ideal for high-resolution imaging. As users embark on the journey to find the best lens, it is imperative to consider factors such as wavelength compatibility, lens shape, and the specific demands of your application to achieve optimal results.
The process of choosing the right Gaas Focus Lens is not just technical but also an art that requires careful consideration and expert insight. By navigating through essential factors and integrating expert recommendations, one can enhance the performance of their optical systems and drive innovation in their respective fields.

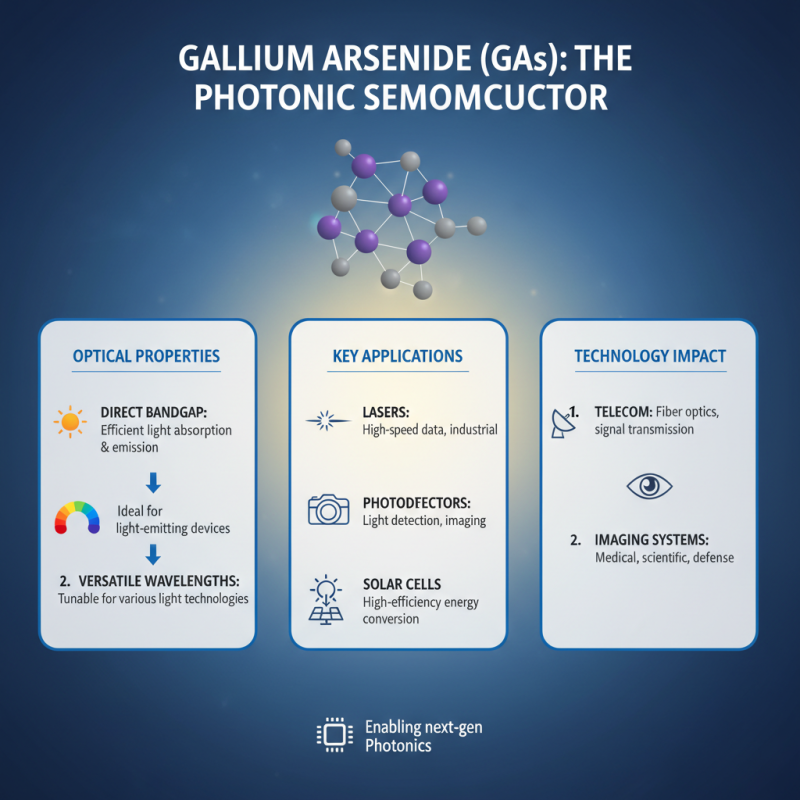
Gallium Arsenide (GaAs) is a compound semiconductor that possesses unique optical properties, making it an essential material in various optical applications. GaAs exhibits a direct bandgap, which allows efficient absorption and emission of light. This characteristic makes it particularly suitable for applications such as lasers and photodetectors, as well as in solar cells where high efficiency is paramount. The material's ability to operate at different wavelengths enables its use in a wide range of optical technologies, from telecommunications to imaging systems.
In addition to its favorable electronic properties, GaAs also demonstrates excellent thermal stability and mechanical strength. These properties contribute to its performance in demanding environments, where other materials might falter. Its high electron mobility enhances the speed of optical devices, allowing for faster data transmission and processing. Furthermore, GaAs lenses can be engineered to minimize losses due to scattering and reflection, thus maximizing light transmission efficiency. Understanding these optical properties is crucial when selecting the best GaAs focus lens for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and reliability in the intended use.
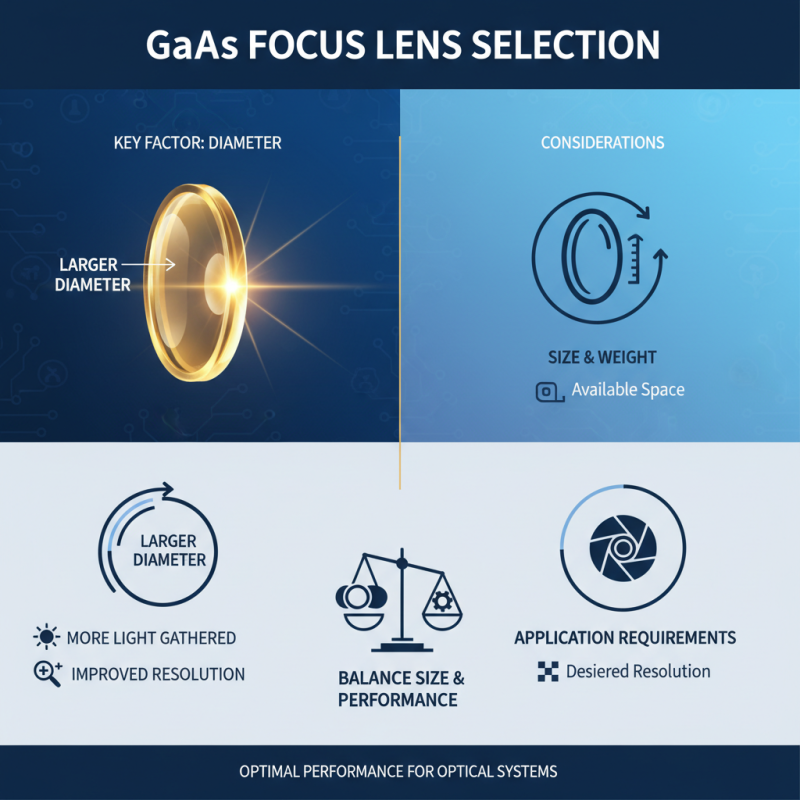
When selecting a GaAs focus lens for optical applications, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance. One critical aspect is the lens diameter, which affects the amount of light that can be gathered and the focal behavior of the lens. A larger diameter typically allows for better light collection but may also increase the physical size and weight of the lens. Therefore, it is essential to balance the size with the specific requirements of your application, such as the available space and desired resolution.
Another significant factor to take into account is the lens coating and its compatibility with the operating wavelength. The coating plays a vital role in minimizing reflection losses and maximizing transmission efficiency. Selecting a lens with the appropriate anti-reflective coating tailored to your application’s wavelength can significantly enhance image quality and overall system performance. Additionally, the material properties of the GaAs lens should be evaluated, including its thermal and mechanical stability, which can influence its effectiveness in high-power or extreme environments. By carefully considering these factors, you can select a GaAs focus lens that best meets the needs of your optical application.
When selecting a GaAs focus lens for optical applications, it's essential to understand the different types available and their specific uses. GaAs lenses are known for their high efficiency in transmitting infrared light, making them ideal for applications such as infrared imaging, telecommunications, and laser systems. The two most common types of GaAs focus lenses are plano-convex and aspheric lenses. Plano-convex lenses are characterized by a flat surface on one side and a convex surface on the other, allowing them to effectively converge light while minimizing spherical aberration. These lenses are typically used in basic optical systems where cost and simplicity are priorities.
Aspheric lenses, on the other hand, feature a more complex surface profile that reduces aberrations across a wider range of wavelengths. They are particularly beneficial in high-performance applications, such as laser focusing and high-resolution imaging systems, where precision is crucial. The design of aspheric lenses enables them to achieve better image quality and efficiency, making them suitable for advanced optical setups. When choosing between these types, consider the specific requirements of your application, including the wavelength of operation, desired focal length, and overall design complexity. An informed choice will enhance the performance and effectiveness of your optical system.
| Lens Type | Material | Wavelength Range (µm) | Applications | Focal Length (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aspheric Lens | GaAs | 0.8 - 1.6 | Laser Focusing, Optical Communications | 25 |
| Spherical Lens | GaAs | 0.9 - 1.4 | Telescopes, Imaging Systems | 50 |
| Fresnel Lens | GaAs | 0.7 - 1.5 | Solar Concentrators, Beam Shaping | 30 |
| Doublet Lens | GaAs Glass | 0.8 - 1.3 | Medical Imaging, Spectroscopy | 40 |
When evaluating GaAs focus lenses for optical applications, several performance metrics are crucial to ensure optimal functionality and efficiency. One of the primary metrics is the lens's optical transmission, which indicates how much light passes through the lens without absorption or scattering. High optical transmission is essential, particularly in applications requiring maximum light coupling or when working with high-intensity light sources. An ideal GaAs focus lens should exhibit a high percentage of transmission across the desired wavelength range, enabling better performance in various optical systems.
Another important performance metric is the focal length of the lens. The focal length determines how sharply images are focused and impacts the depth of field. A shorter focal length provides a wider field of view, whereas a longer focal length can create more magnified images. Additionally, the lens's numerical aperture (NA) should be considered, as it influences resolution and the ability to capture light from wide angles. Understanding these metrics, along with the lens's surface quality, aberration characteristics, and temperature stability, will aid in the selection of the most suitable GaAs focus lens for specific optical applications.
When it comes to the installation of GaAs focus lenses, proper handling is critical to ensure optimal performance. Start by carefully inspecting the lens for any signs of damage or contamination before installation. Clean the lens using appropriate methods; microfiber cloths and dedicated optical cleaning solutions are often recommended. Avoid touching the lens surface with bare fingers to prevent the transfer of oils and dirt. Ensure that the environment is dust-free during installation to minimize the risk of particulates interfering with the optical path.
Maintaining GaAs focus lenses requires a consistent routine to ensure longevity and precision. Regularly check the alignment of the lens within the optical system, as even minor misalignments can lead to degraded performance. Additionally, perform periodic visual inspections for scratches, dust accumulation, or any other imperfections. If the lens exhibits signs of degradation, it’s essential to replace it promptly to maintain the quality of optical applications. Establishing a maintenance schedule can help catch potential issues early, ensuring that your optical systems remain effective and reliable over time.